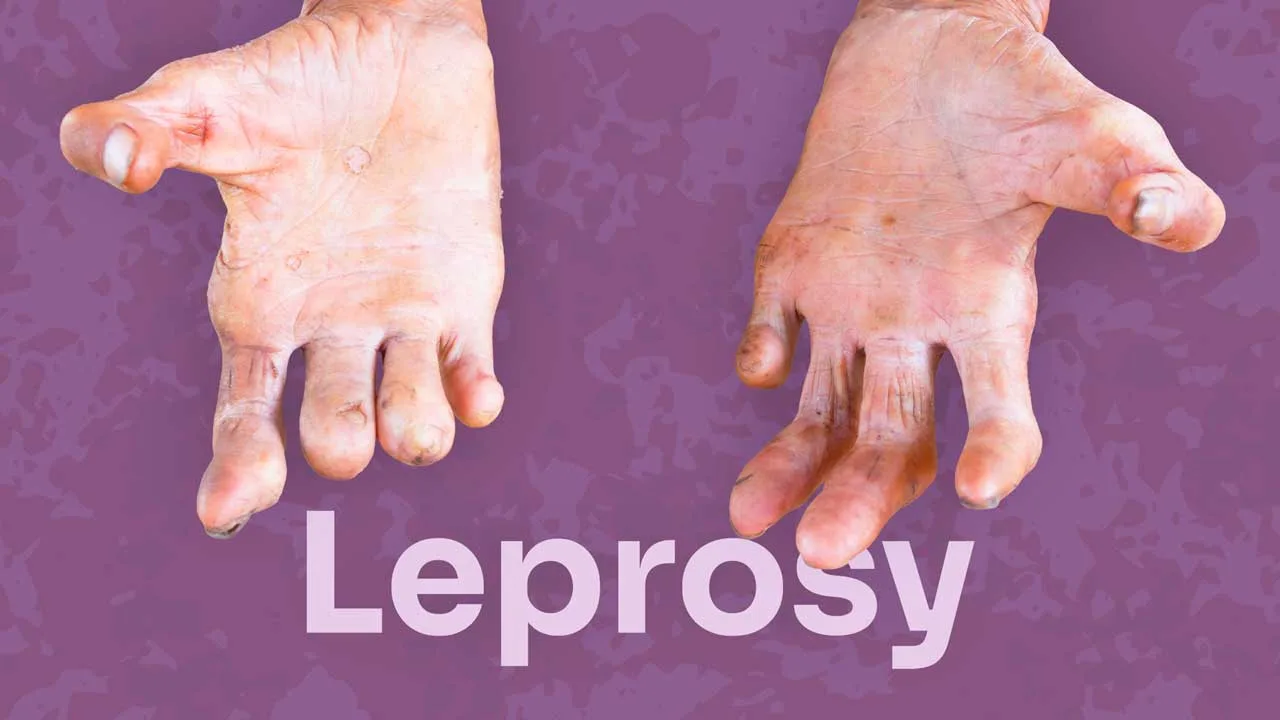
Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused by the slow-growing bacteria Mycobacterium leprae. While the historical image of this disease is often one of disfigurement and social isolation, it’s crucial to understand that leprosy is completely curable with early diagnosis and proper treatment. In fact, due to ongoing efforts by the World Health Organization (WHO) and other health organizations, new cases of leprosy have significantly decreased in recent decades.
Transmission and Symptoms:
Leprosy primarily affects the skin, peripheral nerves, eyes, and the lining of the nose. Transmission occurs through close and prolonged contact with untreated individuals, usually through respiratory droplets from the nose and mouth. It’s important to note that leprosy is not highly contagious, and the vast majority of people have a natural immunity to the bacteria.
Symptoms of leprosy can develop over a long period, ranging from a few years to even decades. The most common signs include:
- Patchy, pale, or numb skin lesions that are lighter than surrounding skin
- Loss of sensation in the affected areas
- Muscle weakness and paralysis, particularly in the hands and feet
- Facial paralysis and drooping eyelids
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent nerve damage and potential disabilities. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination, skin biopsies, and specialized tests. Fortunately, leprosy is highly treatable with a multidrug therapy (MDT) provided by the WHO free of charge. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the case, typically ranging from six to twelve months.
Addressing the Stigma:
Despite the effectiveness of treatment, leprosy still carries a significant stigma in many parts of the world. This stigma often stems from historical misconceptions about the disease being highly contagious and incurable. This stigma can lead to discrimination, social isolation, and limited access to healthcare for individuals affected by leprosy.
It’s crucial to remember that people with leprosy who are undergoing treatment are not contagious. Educational initiatives and community outreach programs are essential to address the stigma surrounding leprosy and create a more inclusive and supportive environment for those affected by the disease.
The Road Ahead:
While significant progress has been made in controlling leprosy, challenges remain. Early detection, accessible treatment for all, and continued efforts to combat stigma are crucial for achieving the WHO’s goal of eliminating leprosy as a public health concern by 2020.
By raising awareness about the true nature of leprosy, we can dispel myths, promote early diagnosis, and ensure that everyone affected by this treatable disease has access to the care they need and deserve.