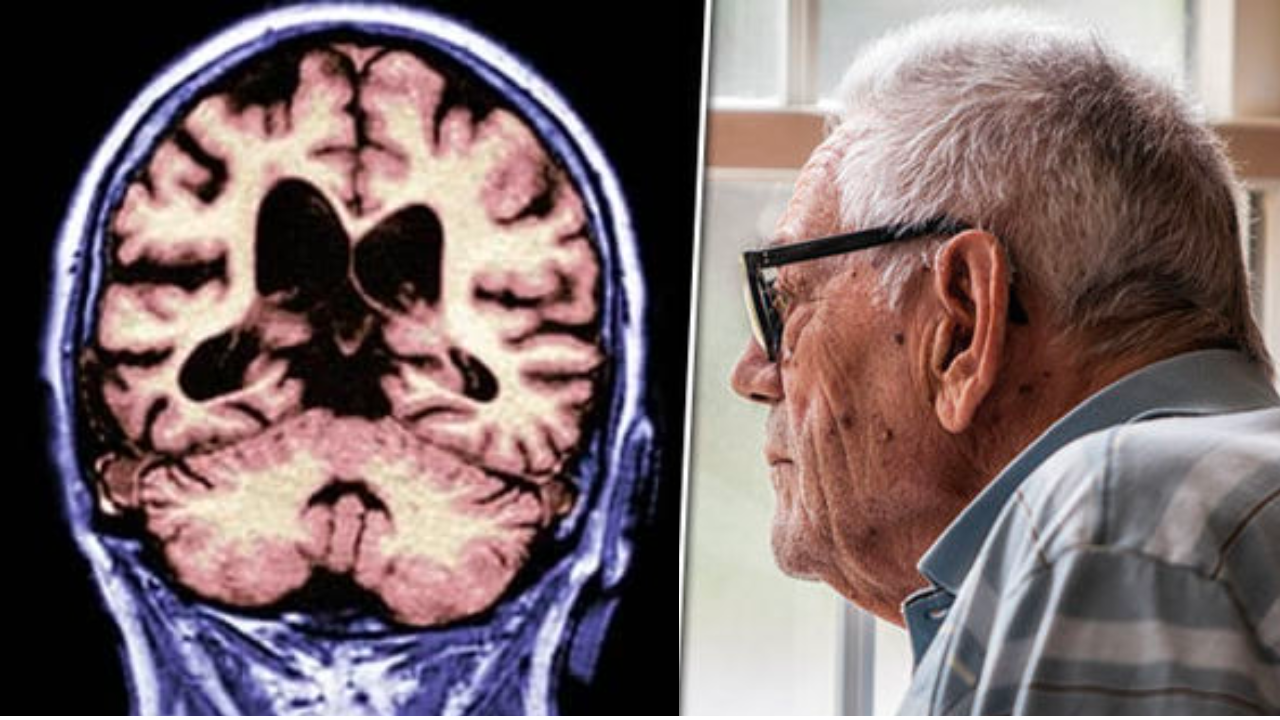
Dementia, often mistakenly equated with mere forgetfulness, is a complex and multifaceted syndrome encompassing a progressive decline in various cognitive functions. It steals not only memories but also the ability to perform daily activities, navigate the world effectively, and maintain meaningful relationships. While not a disease itself, it serves as an umbrella term encompassing various conditions that impact the brain, each presenting unique patterns of decline.
Beyond Memory Loss: A Multifaceted Experience
While memory lapses are often the most recognized symptom, dementia extends far beyond. It can manifest in a constellation of impairments impacting critical cognitive domains:
- Memory: Difficulty recalling recent events, forgetting familiar faces, and struggling to learn new information become increasingly prominent.
- Thinking and problem-solving: Reasoning skills deteriorate, making daily tasks like managing finances or organizing transportation challenging.
- Communication: Speech may become unclear, with individuals struggling to find the right words or express themselves coherently.
- Orientation: Confusion about time, place, and even personal identity can arise, causing disorientation and distress.
- Judgment and decision-making: The ability to make sound decisions regarding personal safety, financial matters, and healthcare needs diminishes.
Lifting the Veil: Unveiling the Underlying Causes
Dementia can occur due to various underlying pathologies, each impacting different brain regions and presenting distinct symptoms. Here’s a glimpse into some of the most common ones:
- Alzheimer’s disease: The most prevalent form, characterized by the abnormal buildup of protein plaques and tangles in the brain, leading to progressive neuronal degeneration.
- Vascular dementia: Caused by impaired blood flow to the brain, often due to strokes or vascular diseases, it primarily affects thinking, problem-solving, and executive function.
- Lewy body dementia: Characterized by abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, it causes fluctuations in cognitive function, along with movement difficulties and hallucinations.
- Frontotemporal dementia: This form impacts the frontal and temporal lobes, leading to personality changes, language difficulties, and social withdrawal.
Navigating the Maze: Diagnosis and Management
While there’s currently no cure for dementia, early diagnosis remains crucial for managing symptoms and maximizing quality of life. This often involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Comprehensive cognitive assessment: Evaluating memory, thinking, and reasoning skills through standardized tests and questionnaires.
- Brain imaging: Techniques like MRI or CT scans can help identify structural abnormalities or vascular issues in the brain.
- Blood tests: Ruling out other medical conditions that may mimic dementia symptoms.
Currently, available treatment options primarily focus on:
- Medications: Certain medications can help manage symptoms like memory decline, agitation, and sleep disturbances.
- Non-pharmacological interventions: Cognitive stimulation therapies, reminiscence activities, and physical exercise can help maintain cognitive function and improve overall well-being.
- Supportive care: Providing emotional support, ensuring safety, and assisting with daily living activities become essential as the condition progresses.
Dementia: A Shared Journey of Hope and Awareness
Dementia can be a daunting journey for both individuals living with the condition and their loved ones. However, it’s crucial to remember that individuals with dementia retain their unique identities and deserve respect and compassion. By raising awareness, fostering understanding, and supporting ongoing research, we can pave the way for better interventions and, hopefully, one day, a cure.
This overview paints a broad picture of dementia. Remember, individual experiences can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause and disease progression. If you suspect someone is struggling with cognitive decline, seek professional advice for a timely and accurate diagnosis.