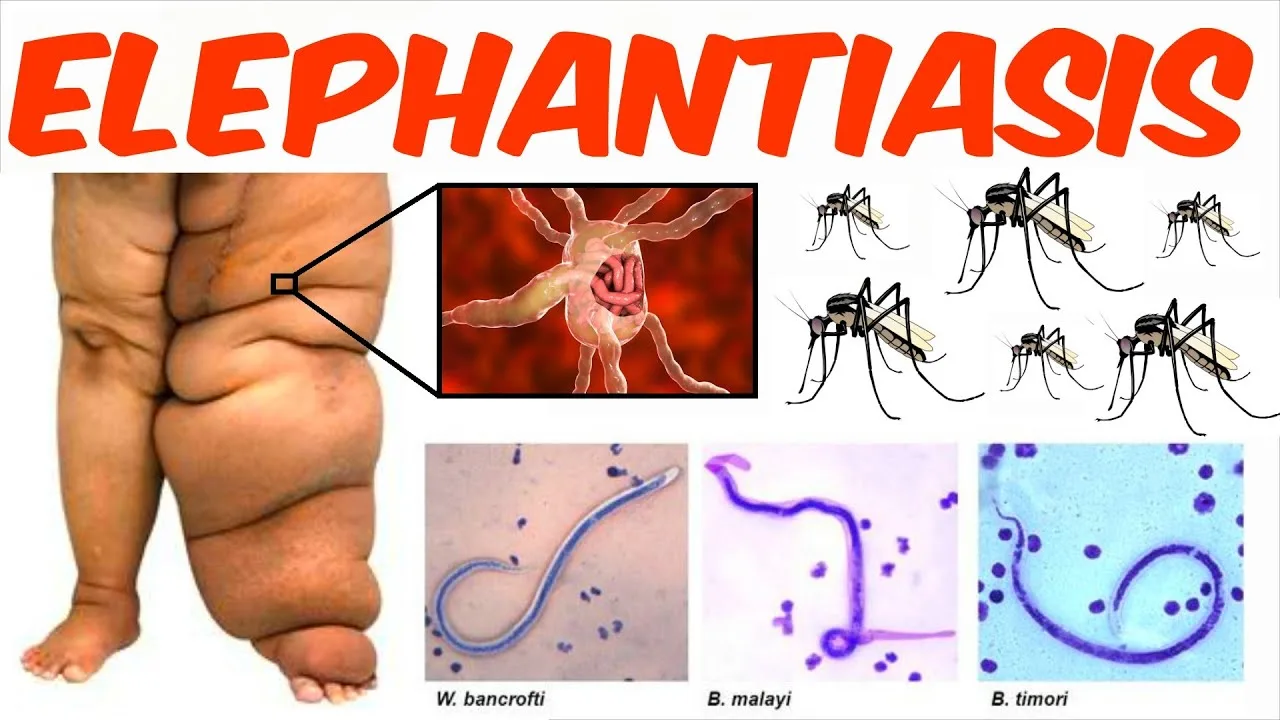
Elephantiasis, also known as lymphatic filariasis, is a nasty tropical disease that causes grotesque swelling in various body parts, most commonly the legs, scrotum, and breasts. Caused by parasitic worms transmitted through mosquito bites, elephantiasis can be a debilitating condition, leading to pain, discomfort, and social stigma. But fear not, here’s a deep dive into this disease, from causes and symptoms to treatment and prevention, empowering you with knowledge to fight back.
Unmasking the Culprit: Filarial Worms and the Lymphatic System’s Woes
The villain behind elephantiasis is a trio of parasitic worms – Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori. These microscopic filarial worms enter your body through infected mosquito bites. They then take up residence in your lymphatic system, a network of vessels crucial for draining fluid waste from tissues. Imagine your lymph system as a city’s sewage system. Now, picture these worms clogging the drains! This is exactly what happens.
The Battle Within: How Elephantiasis Wreaks Havoc
The presence of these worms triggers an inflammatory response in your body. This inflammation damages and blocks your lymphatic vessels, leading to fluid buildup (lymphoedema) in various tissues. This accumulated fluid causes the characteristic swelling – the hallmark sign of elephantiasis. The affected skin can thicken and harden, resembling elephant hide, hence the name.
Symptoms: Beyond the Swelling
While swelling is the most obvious symptom, elephantiasis can manifest in other ways too:
- Fever and chills
- Recurring bacterial infections in the swollen area
- Pain and discomfort
- Difficulty walking or moving the affected limb
- Thickening of the skin and underlying tissues
- Genital swelling in men
Not So Straightforward: Diagnosing Elephantiasis
Diagnosing elephantiasis often involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests to detect filarial worms, and imaging techniques like ultrasound to assess the extent of lymphatic damage. Early diagnosis is crucial for timely treatment and preventing complications.
Fighting Back: Treatment Options for Elephantiasis
There’s no cure for elephantiasis, but treatment can manage symptoms and prevent further complications. Here’s what your doctor might recommend:
- Medications: Antiparasitic drugs to kill the worms and medication to reduce swelling.
- Compression therapy: Using bandages or garments to apply pressure and improve lymphatic drainage.
- Skincare: Maintaining good hygiene and proper skincare to prevent infections in the swollen area.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery might be necessary to remove excess tissue or reconstruct damaged lymphatic vessels.
Prevention is Key: Shielding Yourself from Elephantiasis
The good news is that elephantiasis is preventable! Here are some effective ways to keep yourself safe:
- Mosquito control: Using mosquito nets, repellents, and wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants in areas where elephantiasis is common.
- Mass drug administration (MDA): Participating in MDA programs if offered in your community. These programs involve mass distribution of medication to entire populations to prevent the spread of filarial worms.
- Maintaining hygiene: Practicing good hygiene to prevent secondary bacterial infections in the affected area.
Living with Elephantiasis: Hope and Support
Elephantiasis can be a life-altering condition, but with proper treatment, support, and self-care, people with elephantiasis can lead fulfilling lives. There are also support groups available to connect with others facing similar challenges. Remember, you’re not alone in this fight.
Table: Elephantiasis at a Glance
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Cause | Parasitic filarial worms transmitted by mosquitoes |
| Symptoms | Swelling (legs, scrotum, breasts), fever, chills, pain, difficulty moving |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, blood tests, imaging techniques |
| Treatment | Medications, compression therapy, skincare, surgery (in severe cases) |
| Prevention | Mosquito control, mass drug administration (MDA), hygiene practices |
Remember: Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for managing elephantiasis effectively. If you suspect you or someone you know might have elephantiasis, consult a doctor immediately. By raising awareness and taking preventive measures, we can work towards a future free from elephantiasis.